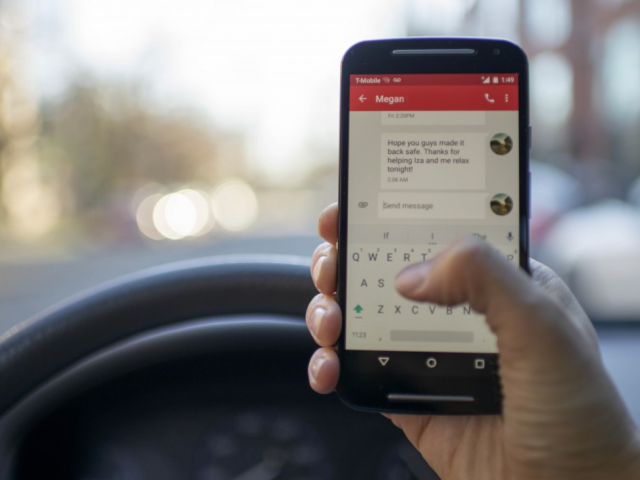
Apple CarPlay and Android Auto infotainment systems weaken reactions more than alcohol and cannabis
A new study by the UK’s transport research laboratory (TRL) shows that the latest in-vehicle infotainment systems that display smartphone apps on in-car displays impair reaction times behind the wheel more than alcohol and cannabis use.
The study found that reaction times at motorway speeds increased average stopping distances to between four and five car lengths. The study also found that drivers took their eyes off the road for as long as 16 seconds while driving (equivalent to a distance of more than 500 metres at 70 mph / 113 km/h), and using touch control resulted in reaction times that were even worse than texting while driving.
Commenting on the findings, Neil Greig, policy and research director of IAM RoadSmart, the organisation that commissioned the study said:
“While previous research indicates that Apple CarPlay and Android Auto perform better than more traditional buttons and controls, the results from this latest study raise some serious concerns about the development and use of the latest in-vehicle infotainment systems. Anything that distracts a driver’s eyes or mind from the road is bad news for road safety.
“We’re now calling on industry and government to openly test and approve such systems and develop consistent standards that genuinely help minimise driver distraction.”
During the study drivers completed a series of three drives on the same simulated test route to assess the level of impact of Android Auto and Apple CarPlay. On the first run, drivers did not interact with the system. On subsequent runs, drivers interacted with the system using voice control only and then using touch control only.
Both methods of control were found to significantly distract drivers, however touchscreen control proved the more distracting of the two. While many drivers realised the system was causing a distraction and modified their behaviour by, for example, slowing down, performance was still adversely affected with drivers unable to maintain a constant distance to the vehicle in front, reacting more slowly to sudden occurrences and deviating outside of their lane.
The key findings from the report are:
– Controlling the vehicle’s position in the lane and keeping a consistent speed and headway to the vehicle in front suffered significantly when interacting with either Android Auto or Apple CarPlay, particularly when using touch control
– Participants failed to react as often to a stimulus on the road ahead when engaging with either Android Auto or Apple CarPlay – with reaction times being more than 50 per cent slower
– Reaction time to a stimulus on the road ahead was slower when selecting music through Spotify while using Android Auto and Apple CarPlay (via touch control rather than voice control), compared to texting while driving (based on previous studies)
– Use of either system via touch control caused drivers to take their eyes off the road for longer than 12 seconds. This does not meet the guidelines set out by NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration). When using voice control all measures were within NHTSA guidelines
– Participants underestimated the time they thought they spent looking away from the road, by as much as five seconds, when engaging with Android Auto and Apple CarPlay via touch control.